The Best 5 Foods to Lower Blood Sugar Quickly (Backed by Science)

If you are searching for the best 5 foods to lower blood sugar quickly, you are in the right place. This guide cuts through the confusion to give you five science-backed, powerful options.
We will explore how common ingredients like apple cider vinegar and cinnamon work to manage glucose levels naturally and effectively.
This isn’t about a temporary fix; it’s about arming yourself with knowledge for lasting metabolic health.
By discovering these readily available foods and learn how to easily incorporate them into your diet to feel more in control of your well-being starting today.
Managing blood sugar is a daily concern for millions. It’s not just about avoiding sugar spikes. It’s about finding foods that actively help you regain balance.
This isn’t about a magical cure.
It’s about smart, science-backed nutritional choices.
Certain foods have powerful properties that can lower blood sugar quickly.
We’ve researched and compiled the five most effective foods.
These choices can help you feel more in control of your health.
Let’s break down The Best 5 Foods to Lower Blood Sugar Quickly (Backed by Science)
1. Apple Cider Vinegar: The Fermented Powerhouse

Research shows Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is a top contender for lowering blood sugar.
Its acetic acid content is the key to its power.
This acid can interfere with enzymes that break down starch.
This means fewer simple sugars enter your bloodstream.
Studies show taking ACV before a meal can improve insulin sensitivity.
It helps your body use sugar more effectively for energy.
How to Use It:
Mix one to two tablespoons in a large glass of water.
Drink it 20 minutes before a carbohydrate-heavy meal.
Never drink it straight, as it can damage tooth enamel.
Also Read: Best Diabetic meal delivery plan
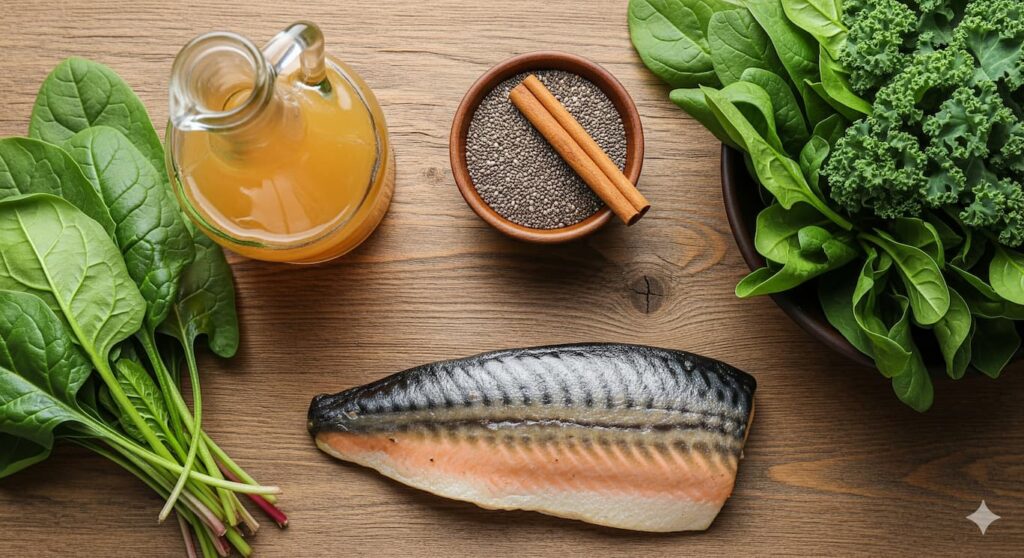
2. Chia Seeds: The Tiny Fiber Giants

Research shows Chia seeds are a nutritional superhero for blood sugar control.
They are incredibly rich in soluble fiber.
This fiber forms a gel when mixed with liquids in your stomach.
This gel slows down digestion dramatically.
It prevents rapid carbohydrate breakdown and sugar absorption.
This leads to a slow, steady release of glucose into your blood.
How to Use Them:
Soak a tablespoon of seeds in water, milk, or yogurt to make pudding.
Sprinkle them on salads, oatmeal, or smoothies.
Their mild taste makes them easy to add to any diet.
Recommended Article: 5 Best Blood sugar supplements
3. Cinnamon: The Sweet-Regulating Spice

Research show Cinnamon is far more than a delicious spice. It contains compounds that mimic the hormone insulin. This helps glucose move from your blood into your cells.
It also slows the emptying of your stomach after eating.
This prevents sharp blood sugar spikes after meals.
Just a small amount can have a significant measurable effect.
How to Use It:
Sprinkle Ceylon cinnamon on your coffee, oatmeal, or yogurt.
Add it to smoothies or rub it on proteins like chicken.
Aim for about half to one teaspoon per day.
4. Leafy Green Vegetables: The Low-Carb Champions

Research Vegetables like spinach, kale, and collard greens are essential.
They are very low in digestible carbohydrates.
This means they add volume to your meal without spiking glucose.
They are also packed with magnesium.
This mineral plays a vital role in insulin function and glucose metabolism.
Eating more greens directly supports your body’s regulatory systems.
How to Use Them:
Make a large salad the base of your lunch or dinner.
Sauté them with garlic and olive oil as a side dish.
Blend them into a green smoothie for a nutrient-packed breakfast.
5. Fatty Fish: The Omega-3 Boost

Research shows Salmon, sardines, and mackerel are excellent choices.
Their power comes from high-quality protein and healthy fats.
Protein and fat slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream.
Protein and Healthy Fats for Blood Sugar Stability (Omega-3s, Fish Protein)
Fish and omega-3s support heart health, reduce inflammation. But trials focusing on salmon or fish protein have had mixed results on blood sugar:
One randomized controlled trial giving salmon fish protein supplement (7.5 g/day) for 8 weeks in adults at risk of type 2 diabetes found no significant effect on 2-hour glucose after an oral glucose tolerance test. PubMed
So while salmon is excellent for overall health, its direct effect on post-meal blood sugar needs more evidence, especially at practical dietary doses.
They are also rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
These fats reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity.
This helps your body use insulin more effectively.
How to Use It:
Aim to eat fatty fish at least two times per week.
Grill, bake, or pan-sear it for a healthy main course.
Add canned salmon or sardines to salads for a quick lunch.
Whole Fruits That Help Lower Blood Sugar
Berries (Blackcurrants, Lingonberries, etc.)
Berries are rich in polyphenols, fiber, and antioxidants. One human crossover meal study had healthy women consume sucrose with whole blackcurrants or lingonberries, and this significantly reduced early glucose and insulin peaks compared to sucrose alone. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Whole Fresh Fruits
A large prospective cohort study over ~3.8 years found that higher intake of whole fresh fruit (especially apples, blueberries, grapes).
This is associated with a reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes in people with normal glucose tolerance. Each 100 g/day of fruit was linked with about 2.8% lower risk. PubMed
Also, nutrient-extraction (keeping fiber) of fruit mixed with others (raspberry/mango etc.) reduces GI in both healthy weight and obese individuals. PubMed
How to Incorporate These Foods Into Your Daily Meals
- Before meals: Try a small handful of almonds (~20 g) 30 minutes before carbohydrate-rich meals.
- Swap refined carbs: Use lentils as part of soups, stews, or as rice replacements.
- Veggie plate: Make non-starchy vegetables (broccoli, greens) half your plate.
- Fruit desserts: Instead of sugary dessert, have berries or fruit mixed with nut butter or yogurt.
- Balanced meals: Combine lean protein (salmon, eggs) + healthy fats (avocado, nuts) + fiber (vegetables, legumes) for stable blood glucose.
You don’t need to eat all five foods at every meal.
The key is consistent integration into your weekly routine.
Start with one or two that appeal to you the most.
Plan a daily salad with leafy greens and a salmon fillet.
Drink ACV water before your biggest meal of the day.
Add cinnamon and chia seeds to your breakfast.
Small, sustainable changes create lasting results.
This approach is far better than a drastic, short-term diet.
Your blood sugar will thank you for the steady support.
Why Lowering Blood Sugar Matters
When blood sugar (glucose) remains elevated, it damages nerves, blood vessels, kidneys, eyes, and increases risk of cardiovascular disease.
For people with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, lowering glucose quickly after a meal (postprandial) is especially important.
Research shows that reducing spikes soon after eating helps prevent long-term complications.
Lifestyle Tips for Sustained Blood Sugar Control
Food is powerful, but it’s only one part of the puzzle.
For lasting results, combine these foods with healthy habits.
Stay hydrated with water to help your kidneys flush excess sugar.
Engage in regular physical activity.
Even a daily 30-minute walk helps your muscles use sugar for energy.
This naturally lowers your blood glucose levels.
Prioritize quality sleep and manage stress.
Poor sleep and high stress increase cortisol.
This hormone can make your blood sugar levels rise.
Foods to Avoid for Better Blood Sugar Levels
Knowing what to avoid is just as important.
Limit refined carbohydrates like white bread and pasta.
These foods break down into sugar very quickly.
Avoid sugary drinks like soda and sweetened juices.
They deliver a massive dose of sugar straight to your bloodstream.
This causes rapid spikes that are hard to manage.
Be cautious with processed snacks and desserts.
They often combine sugar with unhealthy fats.
This is a double burden for your metabolic health.
When to See a Doctor
These foods are excellent for management.
But they are not a substitute for professional medical advice.
If you are consistently experiencing high blood sugar, see a doctor.
They can provide a proper diagnosis.
They will help you create a comprehensive management plan.
This may include medication, diet, and exercise guidance.
Always talk to your doctor before making major dietary changes.
This is especially crucial if you are on diabetes medication.
You want to ensure your new diet works with your treatment.
These 10 Foods Lower Blood Sugar Naturally & Fast
Key Takeaways
- Certain whole foods can help lower blood sugar quickly by slowing digestion, improving insulin sensitivity, or reducing glucose spikes.
- Emphasize non-starchy vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, whole fruits, and lean protein in meals.
- Small, consistent dietary changes supported by research can lead to measurable improvements in blood sugar control.
- Using foods as part of a whole lifestyle—diet, activity, sleep—yields best results.
Conclusion: Empowerment Through Food
You have powerful tools available in your kitchen.
Apple cider vinegar, chia seeds, cinnamon, leafy greens, and fatty fish.
These are the best 5 foods to lower blood sugar quickly.
They work by slowing digestion, improving insulin sensitivity, and providing key nutrients.
Incorporate them wisely into a balanced lifestyle.
You can take significant control of your metabolic health.
Start with one new food this week.
Notice how your body feels after eating it.
This journey is about progress, not perfection.
Best 5 Foods To Lower Blood Sugar Quickly (FAQs)
How quickly can these foods lower blood sugar?
Some, like apple cider vinegar, can have an effect within 30-60 minutes. Others, like cinnamon and chia seeds, work best for sustained control over days and weeks of consistent use.
Can I eat these foods if I am diabetic?
Yes, these are generally excellent choices for a diabetic diet. However, always consult with your doctor or a dietitian to ensure they fit your specific health plan and medications.
Are there any side effects to these foods?
Apple cider vinegar can upset your stomach or harm teeth if not diluted. Cinnamon, specifically the Cassia variety, may be harmful in very large doses due to coumarin content. Moderation is key.
Is fruit bad for blood sugar?
Whole fruits contain fiber that slows sugar absorption, making them a better choice than juice. Berries, apples, and citrus fruits are generally good options in moderation.
Do I need to eat special or expensive foods?
No. The best foods are often whole, simple, and affordable. Leafy greens, cinnamon, and seeds are accessible and don’t require a special diet or high cost.
Will these foods work for prediabetes?
Absolutely. These foods are a cornerstone of dietary strategies to manage and reverse prediabetes by improving insulin sensitivity and preventing blood sugar spikes.
Can I stop my medication if I eat these foods?
No. Never stop or change your medication dosage without direct supervision from your doctor. These foods are a supportive tool, not a replacement for prescribed medical treatment.
What foods lower blood sugar immediately?
Foods high in fiber and with low glycemic index help—such as almonds before meals, lentils, and non-starchy vegetables. These slow down sugar absorption and blunt spikes.
How much almonds do you need to see an effect?
Studies used about 20 g almonds (roughly a small handful) before main meals, for 2-3 months. More doesn’t always improve results; balance and portion matter. ScienceDirect+1
Are fruit juices bad for blood sugar?
Juices often lack fiber, causing quicker sugar absorption and higher blood sugar spikes. Studies show that whole fruits (or fruits prepared to retain fiber) have lower glycemic impact than juices. PubMed
Can broccoli extract really help?
Yes, a broccoli sprout extract (sulforaphane) trial in prediabetes showed a small but statistically significant drop in fasting blood sugar over 12 weeks. PubMed
Do chia seeds reliably lower blood sugar?
So far, evidence is inconsistent. Some animal studies show benefit; human meta-analyses usually show no significant impact on fasting glucose or HbA1c. ScienceDirect+1
Is there any one food that works best for everyone?
No. Responses differ due to genetics, gut microbiome, overall diet, and stage of glucose intolerance. Combining several good foods tends to work better than relying on a single “superfood.”
Should I avoid all carbs?
Not necessarily. Carbohydrates from whole grains, legumes, fruits can be part of a healthy diet. Avoid refined carbs and sugars, but include complex carbs with fiber to moderate blood sugar.