Gestational Diabetes Meal Plan: How to Eat Well for You and Your Baby
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy. It affects how the body processes sugar. Managing it with a healthy diet is crucial for both mother and baby.
This gestational diabetes healthy diet article covers everything you need to know about maintaining a healthy diet if you have gestational diabetes.
Key Takeaways
- Understand Gestational Diabetes: Learn what it is, symptoms, and diagnosis.
- Diet’s Role: Discover how diet affects gestational diabetes.
- Healthy Diet Components: Key nutrients to include in your diet.
- Meal Planning Tips: Practical tips and sample meal plans.
- Foods to Avoid: Understand what to avoid for better health.
- Physical Activity: Importance of exercise in managing gestational diabetes.
- Professional Support: Working with healthcare professionals.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It affects how your body uses glucose, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Unlike other types of diabetes, gestational diabetes is temporary and usually resolves after childbirth. However, it can pose risks to both mother and baby if not managed properly.
Causes and Risk Factors: Gestational diabetes occurs when your body can’t produce enough insulin during pregnancy. Hormonal changes and weight gain increase insulin resistance.
Risk factors include being overweight, a history of gestational diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and a family history of diabetes. Age also plays a role; women over 25 are at a higher risk.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
Common Symptoms: Many women with gestational diabetes experience no noticeable symptoms. Regular prenatal screenings are vital.
However, some may experience excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and nausea. If you notice these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider for testing.
Diagnosis Process: Gestational diabetes is typically diagnosed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. The process involves a glucose screening test, followed by a glucose tolerance test if needed.
Early detection and management are crucial to reduce risks for both mother and baby.
Why Diet is Crucial in Managing Gestational Diabetes
Impact of Diet on Blood Sugar Levels: A healthy diet helps control blood sugar levels. Eating the right foods in the right amounts can keep your blood sugar stable.
This helps reduce risks associated with gestational diabetes. A balanced diet also supports your baby’s growth and development.
Benefits of a Healthy Diet: Following a healthy diet during pregnancy can prevent complications such as high birth weight, preterm birth, and the development of type 2 diabetes later in life.
It also promotes overall well-being and energy levels, making pregnancy more comfortable.
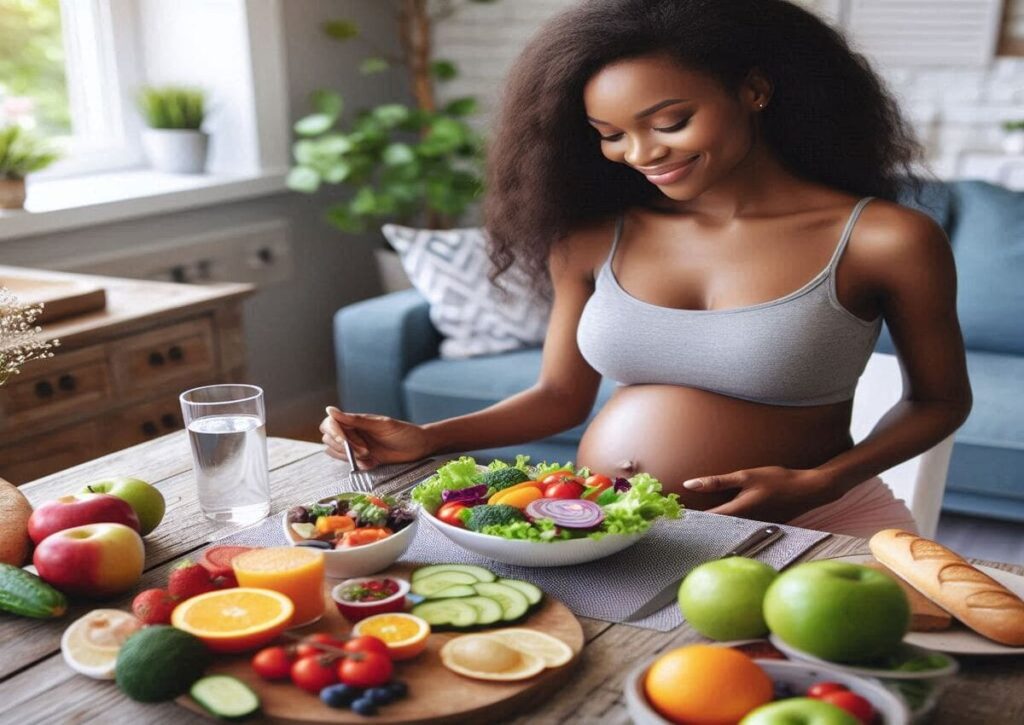

Key Components of a Healthy Diet for Gestational Diabetes
Carbohydrates
Types and Effects: Carbohydrates impact blood sugar levels the most. Choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, vegetables, and legumes. These provide steady energy and are less likely to cause spikes in blood sugar.
Recommended Intake: Aim for balanced meals with 45-60% of calories from carbohydrates. Spread intake evenly throughout the day to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Proteins
Importance in Diet: Proteins are essential for the growth and repair of tissues. They also help you feel full, which can prevent overeating.
Sources: Include lean proteins such as chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, beans, and low-fat dairy. These options are nutrient-dense and beneficial for both mother and baby.
Fats
Role of Healthy Fats: Healthy fats support brain development and hormone production. They also help with the absorption of vitamins.
Examples of Good Fats: Include sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Avoid trans fats and limit saturated fats found in fried and processed foods.
Fiber
Benefits of Fiber: Fiber aids digestion and helps control blood sugar levels. It also helps you feel full, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
High-Fiber Foods: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into your diet. These foods are rich in fiber and provide essential nutrients.
Practical Meal Planning Tips for Gestational Diabetes

How to Plan Balanced Meals
Balancing Nutrients: Ensure each meal contains a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Portion Control and Timing: Eat smaller, more frequent meals to avoid blood sugar spikes. Include snacks if needed to maintain energy levels.
Sample Meal Plans – Gestational Diabetes Healthy Diet
Daily Meal Plan Example:
- Breakfast: Whole grain toast with avocado and a boiled egg.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens and quinoa.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted vegetables and brown rice.
- Snacks: Greek yogurt with berries, carrot sticks with hummus.
Creating Your Own Plan: Customize your meal plan based on your preferences and dietary needs. Consult with a dietitian if needed for personalized advice.
Healthy Recipes for Gestational Diabetes
Breakfast Ideas:
- Oatmeal with chia seeds and fresh fruit.
- Smoothie with spinach, banana, and almond milk.
Lunch and Dinner Ideas:
- Lentil soup with whole grain bread.
- Stir-fried vegetables with tofu and brown rice.
Snack Ideas:
- Apple slices with peanut butter.
- Cottage cheese with sliced cucumber.
Foods to Avoid When You Have Gestational Diabetes
Sugary Foods and Drinks
High-Sugar Risks: Sugary foods and drinks cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Avoid soda, candy, pastries, and sweetened beverages.
Alternatives: Opt for water, herbal teas, and naturally sweetened foods like fruits. Use spices like cinnamon to add flavor without sugar.
Refined Carbohydrates
Impact on Blood Sugar: Refined carbohydrates like white bread, pasta, and rice can cause blood sugar levels to rise quickly. They lack fiber and essential nutrients.
Healthier Choices: Choose whole grain alternatives such as whole wheat bread, brown rice, and whole grain pasta. These options have more fiber and nutrients.
Processed Foods
Dangers of Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain unhealthy fats, sugars, and additives. They can contribute to weight gain and high blood sugar levels.
Healthier Alternatives: Prepare meals at home using fresh ingredients. This allows you to control what goes into your food and ensure it’s healthy.

Managing Cravings and Staying Motivated on a Gestational Diabetes Diet
Dealing with Sugar Cravings
Tips and Strategies: Cravings can be challenging, but it’s important to manage them. Eat balanced meals to keep your blood sugar stable. This can help reduce cravings. Drink plenty of water and stay hydrated. Sometimes thirst is mistaken for hunger.
Healthy Alternatives: When cravings hit, choose healthy snacks. For a sweet fix, have a piece of fruit or a small serving of dark chocolate. Avoid keeping unhealthy snacks at home to reduce temptation.
Staying Motivated
Support from Family and Friends: Having a support system can make a big difference. Share your dietary goals with your loved ones. They can offer encouragement and help you stay on track.
Tips for Staying on Track: Set realistic goals and celebrate small achievements. Keep a food diary to track your meals and monitor your progress. Remember that every healthy choice you make benefits both you and your baby.
The Role of Physical Activity in Managing Gestational Diabetes
Benefits of Regular Exercise: Exercise helps control blood sugar levels and promotes overall health. It can also reduce stress and improve your mood. Regular physical activity is beneficial for both mother and baby.
Safe Exercises for Pregnant Women: Choose low-impact activities that are safe during pregnancy. Walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga are excellent options. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise routine.
Incorporating Activity into Daily Routine: Find ways to stay active throughout the day. Take short walks after meals, use the stairs instead of the elevator, and do gentle stretching exercises at home. Consistency is key to reaping the benefits of physical activity.
The Importance of Working with Healthcare Professionals
Regular Check-Ups and Monitoring
Medical Check-Ups: Regular check-ups are crucial for managing gestational diabetes. Your healthcare provider will monitor your blood sugar levels and overall health. Follow their advice and attend all scheduled appointments.
Home Monitoring: You may need to monitor your blood sugar levels at home. Use a blood glucose meter to check your levels as recommended by your healthcare provider. Keep a record of your readings to share during check-ups.
Dietitian and Nutritionist Support
Benefits of Professional Support: A dietitian can provide personalized dietary advice. They can help you create a meal plan that meets your nutritional needs and manages your blood sugar levels.
Finding the Right Nutritionist: Look for a registered dietitian with experience in gestational diabetes. Your healthcare provider can recommend a qualified professional. Working with a nutritionist can make managing your diet easier and more effective.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gestational Diabetes and Diet
Can Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented?
While it can’t always be prevented, maintaining a healthy weight with standard meal plan and eating a balanced diet can reduce your risk. Regular physical activity also helps.
What Are the Long-Term Effects on the Baby?
Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may have a higher birth weight. They are also at risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Proper management during pregnancy can reduce these risks.
Can Gestational Diabetes Go Away After Pregnancy?
Yes, gestational diabetes usually goes away after childbirth. However, it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. Continue healthy habits postpartum to reduce this risk.
How Does Gestational Diabetes Affect Delivery and Labor?
It can lead to complications such as a higher likelihood of cesarean delivery. Monitoring and managing blood sugar levels can help ensure a safer delivery.
Conclusion: Maintaining a Healthy Diet with Gestational Diabetes
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for managing gestational diabetes. It helps control blood sugar levels and supports the health of both mother and baby.
Follow the dietary guidelines, stay active, and work with healthcare professionals to manage your condition effectively. With proper management, you can have a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby.
Additional Resources for Managing Gestational Diabetes
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Nutrition Tips for Pregnancy
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Gestational Diabetes
Take Charge of Your Health
Implement the tips and advice shared in this article to manage your gestational diabetes effectively. Remember, your health and your baby’s health are worth the effort. Stay committed, seek support, and make healthy choices every day.
Note:
Please consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your diet or exercise routine. This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.